
The utility industry is the lifeline of our cities, carrying power from remote, wind-swept plains to bustling urban centres. But this vital lifeline is facing a major challenge. As climate change intensifies, with events like wildfires or forest fires raging and heatwaves soaring becoming more frequent, the urgency to transition to clean energy and decarbonize has never been greater. Renewable Energy Sources (RES) are expected to supply 45–50% of global power by 2030, a clean energy surge fuelled by environmental concerns and economic growth.
Yet, today’s ageing grid infrastructure struggles to accommodate the increasing demand and volatile nature of renewable energy. Built for a slower-paced energy landscape, the current grid faces significant challenges, with tools and systems designed for more predictable demands. To bridge the gap, utilities need up to 10,100 miles of new high-capacity lines each year—a costly, complex expansion hindered by regulatory hurdles. The task is clear: modernise and expand to power a cleaner, more resilient future.
In short, the utility sector, traditionally known for stability and slow evolution, is now at a crossroads with unprecedented challenges and opportunities that demand urgent action and adaptability, such as:

- Ageing infrastructure: Decades-old grids weren’t built for today’s energy demands.
- Demand fluctuations and load management: Energy demands can surge in seconds due to extreme weather or shifting patterns, risking grid overload.
- Renewables integration: Solar and wind energy, though clean, are highly variable. Integrating them without disrupting the grid requires constant adjustments. As renewable energy grows, the lack of real-time insights to manage low-voltage distribution networks can lead to instability, affecting reliability and causing voltage and frequency issues.
- Cybersecurity: As the grid becomes more connected, it also becomes more vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
- Cost control and efficiency: Without real-time data, energy distribution can be inefficient and costly.
- Regulatory compliance: Safety, environmental standards, and reliability regulations are stricter than ever.
- Siloed systems and high latency: Many utilities operate multiple systems that limit visibility and slow their ability to adapt to market demands.
- Operational disruptions and unplanned failures: Unexpected maintenance disrupts service, increases costs, and hurts revenue.
- Grid reliability and outage prevention: Power outages bring cities to a halt.
Given the above, how can electric utilities navigate this complex landscape and swiftly adapt while ensuring seamless operations and compliance? Real-time electric utility monitoring is the answer. Let’s see how.
Real-time utility monitoring: A 360° view of your power infrastructure & operations
Real-time monitoring of electric utilities gives utility providers a 24/7 pulse on their entire network. You can have instant insights into every substation, transformer, and power line—you will know exactly where power is flowing smoothly and where it’s facing hiccups.
80% of businesses see revenue growth with real-time data. Similarly, utility monitoring offers providers real-time insights into their operations, implying they can detect issues the moment they arise, preventing minor disruptions from turning into large-scale outages and boosting performance and revenue.
Real-time monitoring is transformative for both the broader grid and individual facilities, offering a dual advantage that amplifies efficiency across the energy landscape.
- Grid level: By analysing data from various grid components, such as substations, transformers, and power lines, utility providers can improve grid reliability, optimise operations, enhance customer service, and integrate renewable energy.
- Facility level: On a smaller scale, buildings and facilities gain real-time insights into their energy usage, enabling smarter consumption, cost savings, and a lower environmental footprint.
This dual benefit means real-time monitoring not only ensures reliable energy flow at a macro level but also optimises usage at each facility—driving efficiency, sustainability, and superefficient energy management everywhere.
So, the big question is, how do we implement real-time monitoring in the electric utilities sector? Digital tools are the answer.
Real-time insights: Powering the future of electric utilities
Today’s digital advancements give electric utilities a powerful toolkit for real-time monitoring, leading to significant benefits across the board. As demonstrated by McKinsey’s findings, leading utilities are already reaping the rewards.
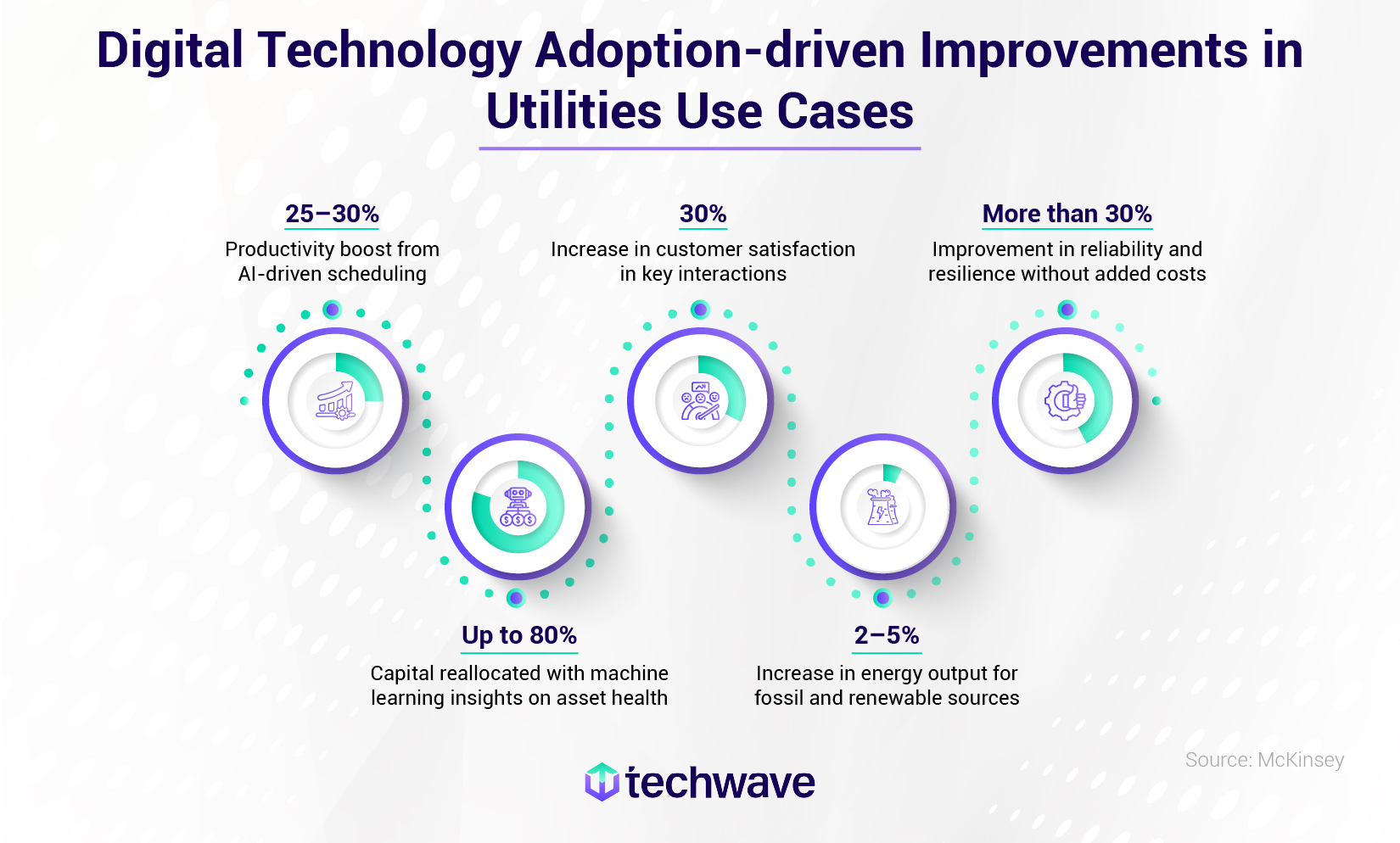
These impressive results underscore the transformative potential of digital tools and highlight the potential for growth, efficiency, and resilience across the utility sector.
But here’s the catch: while some utilities are beginning to embrace these tools, many struggle to keep up with the fast-evolving technology landscape. This lag means missed opportunities to improve resilience, customer service, and cost efficiency that could have helped adapt to the evolving energy landscape. To stay competitive and future-proof their operations, utilities must embrace digital transformation. Real-time monitoring systems, powered by a complex interplay of technologies, provide the granular data needed to make informed decisions. Let’s delve deeper into the key technologies enabling real-time monitoring.
1.Role of AI and ML in data analytics
74% of energy and utility companies are leveraging or planning to leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI). By tapping into vast data streams from smart grids, AI drives innovation in operational management and resilience, creating smarter, more sustainable energy systems. How exactly does it work?
AI, when combined with real-time sensor data from smart grids, empowers energy operators to make faster, more informed decisions. By analysing data from distributed generators, transmission networks, and energy consumption patterns, AI optimises efficiency and bolsters grid security, ensuring a reliable and resilient energy supply. Key AI applications in grid management include:
- Intelligent Predictive Site Maintenance Schedule: Optimized potential field personnel performing site visits by 60%. Provides data visualization for easy consumption of insights and actionable decision-making.
- Energy demand forecasting: AI predicts energy consumption patterns with high accuracy, optimising resource allocation, and responding to demand spikes. It directs power where it’s needed most, reducing blackout risks.
- Predictive maintenance: AI analyses data to forecast equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance that minimises unexpected downtime, cuts repair costs, and improves reliability.
- Renewable energy integration: AI helps provide consistent renewable energy by forecasting generation from sources like solar power and wind turbines. It ensures a stable power supply and improves grid expansion planning.
- Smart homes & buildings: AI, combined with the Internet of Things (IoT), transforms homes and buildings into energy-efficient ecosystems, optimising real-time energy usage.
Given the wildfire problem across the western U.S., parts of Europe and Australia, utility companies are using AI to safeguard power lines. One such climate startup combines weather and vegetation data to predict and prevent grid disruptions, reducing outages by 30% and outage duration by 55%!
2. Advanced sensors and IoT devices
Electric utilities are shifting from manual monitoring to smart, data-driven strategies.
Real-time monitoring, powered by IoT and sensor networks, revolutionises grid management by connecting assets across the network, providing real-time insights. It enables the seamless collection and transmission of data from a vast array of devices, including:
- Smart meters: These advanced devices provide granular data on electricity consumption, enabling utilities to identify patterns, trends and anomalies.
- Temperature and humidity sensors: Excessive heat or humidity can lead to equipment failure. IoT sensors monitor temperature and humidity in equipment like transformers and switchgear, preventing failures from excessive heat or moisture. Environmental monitoring in substations and control rooms ensures optimal conditions, extending equipment life and supporting reliable operations.
- Vibration sensors: Vibration sensors can detect early signs of mechanical wear and tear in rotating equipment like turbines and generators. By identifying potential issues before they escalate, utilities can schedule preventive maintenance, reducing the risk of unplanned outages.
- Safety detectors: These sensors can help monitor hazards, leaks in substations and other facilities. Immediate alerts enable utilities to respond swiftly, mitigating risks and ensuring worker safety.
Sensors offer a real-time dashboard of asset status, alerting operators to issues through customisable automated alarms, ensuring quick responses. When alarms trigger, detailed data enables fast, informed decisions. Stored sensor data supports predictive maintenance, highlighting trends for prioritised repairs and upgrades. This data also feeds into an asset health index, tracking equipment conditions for proactive maintenance or replacement. IoT and sensor networks empower electric utilities to enhance reliability, extend asset life, and optimise efficiency.
A U.S. utility installed sensors on two 230-kilovolt lines for under $300,000, boosting line capacity by 18% and cutting congestion costs from over $60 million to $1.6 million— avoiding a $50 million reconductoring project!
Seamless device communications, such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi, are also available for effective real-time energy monitoring. These enable data transmission from sensors to central monitoring systems.
3. Edge computing for fast data processing
Imagine a network of smart devices scattered across the grid. These devices, equipped with sensors, gather critical data like voltage levels, current flow, and temperature readings. Traditionally, all that data would travel to a central server for processing, slowing decision-making and creating potential risks. But today, with edge computing (another layer of IoT), the grid can think faster and smarter right where the data is generated (implying data sources like sensors, meters, etc.). Instead of flooding the cloud with massive data streams from thousands of IoT sensors, edge devices process data locally (closer to its source), thereby offering the following benefits:
- Ensures near-instant updates on critical grid conditions—monitoring voltage, frequency, and equipment health
- Quicker responses to grid issues, reducing downtime, and easing the strain on network resources; also prevents cascading outages
- Can detect early signs of equipment failure and perform proactive maintenance, preventing costly breakdowns and unplanned downtime
- Empowers utilities to analyse data locally, enabling smarter decisions about maintenance schedules, operational adjustments, and resource allocation
For example, Smart Wires’ Advanced Power Flow Control (APFC) technology showcases edge computing in action.National Grid (an energy company operating in the UK and US) used edge computing to enhance grid management, allowing real-time data processing from IoT devices like sensors, smart meters, and automated switches. By deploying intelligent devices at key points in the grid, APFC enables real-time power flow control, boosting grid stability and efficiency.
Techwave: Your partner in transforming electric utilities with real-time intelligence
While real-time monitoring technologies are advancing for electric utilities, some challenges remain. Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive grid data and user information is critical yet difficult to achieve. Modernising legacy infrastructure to integrate seamlessly with new technologies can be complex and costly. Additionally, training utility staff to operate advanced systems requires significant investment in upskilling.
Addressing these obstacles is essential for fully harnessing the power of innovation in utilities. If you’ve implemented digital technologies for real-time monitoring and seen early benefits but are still facing challenges, it’s time to partner with Techwave.
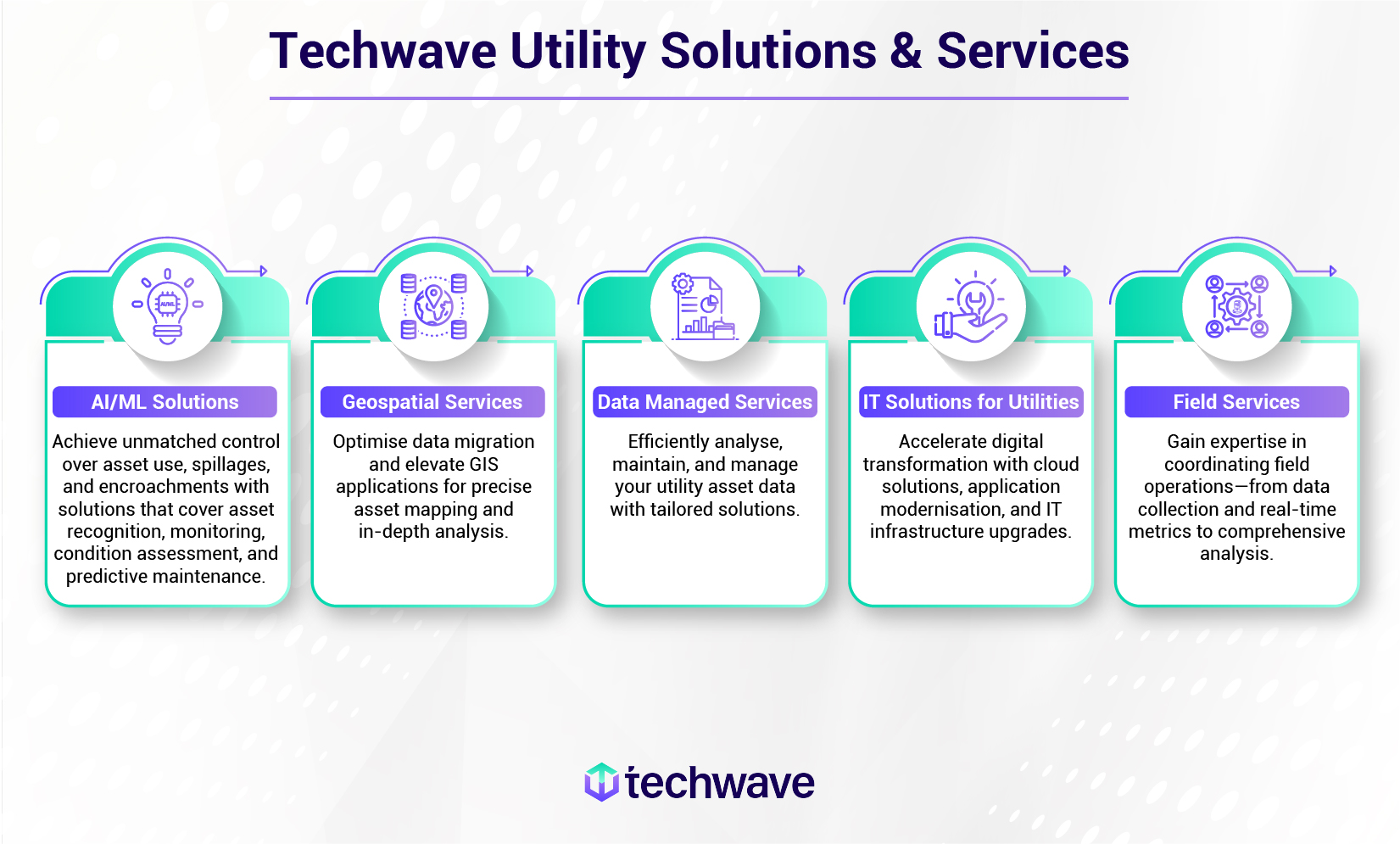
Driven by innovation, sustainability, and strategic resource optimisation, we empower enterprises to shape a smarter, more sustainable tomorrow. Techwave can help you navigate the complexities of digital transformation and overcome the challenges of real-time monitoring. Our comprehensive suite of solutions, from AI-powered insights to advanced data management, empowers you to unlock the full potential of your infrastructure, achieve operational excellence, and build a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy future.
Contact us today to learn how Techwave can help you realise this vision.
