ISO 20022: An In-depth Look at the Global Messaging Standard
The payment industry has made remarkable strides, becoming faster, more efficient, and inclusive, all in response to customer preferences. However, it now finds itself at another critical juncture, grappling with intense competition, an influx of new players, and significant technological advancements and regulatory changes.
According to McKinsey, the global payments revenue 2020 amounted to nearly $2 trillion. However, estimates now indicate it will reach $3 trillion by 2026.
Financial institutions have created distinct standards in the past, each using its own language. When significant sums of money are at stake, miscommunication between banks poses a substantial risk. The challenge intensifies when institutions in different regions adopt varying standards for communicating these transactions, making it difficult to streamline and synchronize global banking operations.
The lack of genuine and universal standardization in payment messaging, i.e., the absence of a shared, common language hinders the swiftness of transaction processing in cross-border payments and alternative bank payment methods.
The ISO 20022 format effectively addresses this concern by establishing a common language, bridging the gap caused by varying standards. It is an internationally recognized financial service messaging standard designed to become a universal, well-structured messaging scheme for the finance industry.
ISO 20022 makes it easier for companies to communicate with their banks consistently. It provides a unified model across various business domains, including payments, securities, trade and card services, and foreign exchange (FX). It also serves as a guideline for all participants in cross-border communication. As a shared foundation, it enables service providers worldwide to develop new services and continuously enhance user experiences.
The Need to Move from SWIFT MT to ISO 20022 MX Messages
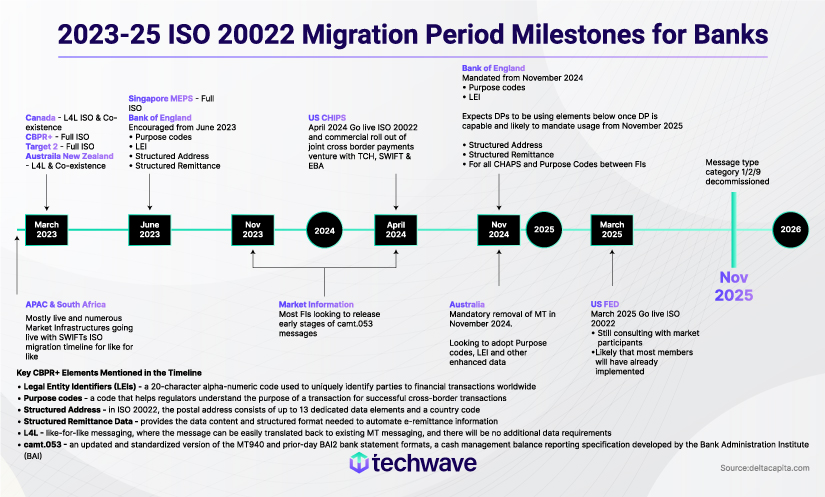
On March 20, 2023, the Cross-Border Payments and Reporting (CBPR+) migration to the ISO 20022 standard began successfully, marking a landmark achievement for the global payments sector. SWIFT MT (message text) and ISO 20022 message formats (MX-message text in XML format) will coexist until November 2025, the deadline SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications) set. After this deadline, most MT messages will no longer be allowed. By 2025, ISO 20022 will become the universal standard for high or large-value payment systems involving all reserve currencies.
This SWIFT ISO 20022 migration, facilitated by CBPR+, is part of an initiative to establish a unified standardization approach for all financial standards initiatives to create a new global payment standard.
The CBPR+ exchanges encompass more than 1,000 BICs on the sending side and over 5,000 BICs on the receiving side. Notably, one-quarter of the received traffic is in ISO 20022 format, and this conversion is achieved without any intervention from the in-flow translation service.
Although SWIFT has introduced many changes and innovations to the traditional MT messaging system, the evolving financial markets have demanded more than the original design. Consequently, most firms had to customize MT messages to address their specific needs. For example, field 72 in an MT103 has been extended to accommodate relevant payment information that doesn’t fit within the standard fields of the message.
In response, the industry has decided to entirely replace the old MT standards with MX messages because they comply with ISO 20022 standards. Adopting the MX format will be progressive but will depend on the speed of its adoption by countries or regions. The transition from the legacy MT messaging to the data-rich ISO MX standard represents a positive step toward innovation.
Those institutions that do not migrate to ISO 20022 cannot match competitors’ services; they risk incompatibility and lag in the industry, potentially losing global customers. Also, non-compliant banks risk payment inefficiencies due to manual interventions, Straight-through Processing (STP) issues, and compliance challenges.
Real-time gross settlement systems (RTGSs) in many significant domestic markets, including Australia, Canada, Europe, and New Zealand, began migrating to ISO 20022 on March 20, with more to follow in the coming months and years.
Data Integration Redefined: Transforming Payment and Banking Services with Data-driven Insights
The implementation of ISO 20022 has redefined data integration, offering significant opportunities to extract maximum value from financial transactions and data within the financial industry. It ensures that all relevant ISO payment-related information, such as payment amount, currency, beneficiary information, payment purpose, payment initiation date, etc., is captured in a consistent format, regardless of the underlying payment system or network.
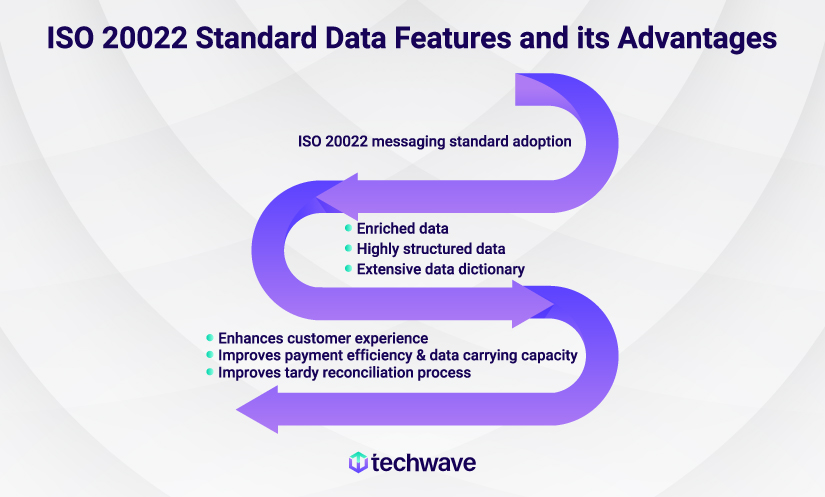
ISO 20022 has enhanced data quality by providing the following:
- Enriched data: This includes adding new fields and more comprehensive information within the existing fields, resulting in a richer dataset for financial transactions.
- Highly structured data: ISO 20022 defines a well-structured format for presenting information, ensuring a standardized and consistent approach to data representation.
- Extensive data dictionary: The updated messaging standard is a comprehensive data library for essential business terms, including crucial payment terms that can be universally reused. The ISO 20022 message model enables organizations to create globally applicable messages. Data dictionaries enhance interoperability and reduce ambiguity in message processing.
Given the above-mentioned data quality features, ISO 20022 offers an extensive dataset that can be integrated to provide a 360-degree view of customer journeys and enhance the credibility of financial institutions resulting in numerous advantages and opportunities as explained below.
● Enhances customer experience
With access to granular data, financial institutions can develop better services and customize products based on deeper insights into customers’ preferences and requirements.
For example, traditional credit scoring methods often overlook large groups of individuals who lack conventional spending habits or credit histories, even though they can comfortably repay loans. ISO 20022 ecosystem opens the door to a broader array of datasets, allowing financial institutions to assess a customer’s creditworthiness more comprehensively.
● Improves payment efficiency & data carrying capacity
Increased data granularity improves the accuracy and efficiency of payment processing, facilitating faster and more reliable settlement. The ISO 20022 data standard uses an extensible markup language (XML) format that is descriptive and user-friendly. The MX message type is an XML-based alternative to the MT message type. MX messages are notably longer than existing MT messages, capturing more data with a hierarchical structure that enables logical data grouping.
For example, ISO 20022 standard introduces new data fields that offer additional transaction details, such as payment purpose, type, and associated fees, enhancing the overall payment experience.
● Improves tardy reconciliation process
The limited space in MT formats can lead to truncated or lost remittance information, causing payment processing delays and potential transaction rejections. In contrast, ISO 20022’s dedicated element structure allows specific business data instructions, creating a dynamic and enhanced data model.
These structured elements promote interoperability and smooth message exchange between regions. ISO 20022 introduces new features like extended remittance information, which primarily exists in free format in the current MT format and poses challenges for proper tagging.
Revolutionizing Cross-Border Payments: Achieving Global Interoperability with ISO 20022
Traditional money transfer methods across borders have evolved significantly. Initially, people used three methods:
- Physical cash
- Using acquaintances or couriers
- Trust-based broker networks
However, these communication networks alone couldn’t solve the prerequisite for reliable cross-border payments infrastructure. Currencies as closed-loop systems hindered moving money between domestic payment systems in different countries. The solution was correspondent banking.
But international payments to all countries and banks globally still present a challenge. Establishing branches everywhere or managing numerous direct relationships and accounts are complex tasks, even for the most prominent international banks.
Currently, cross-border transactions banking rely on fragmented standards, leading to challenges in managing communication between Financial Market Infrastructures (FMIs), Financial Institutions (FIs), and Machines. Sending money across borders comes with unique challenges, including:
- Data security & fraud prevention
- Lack of transparency in international payments
- Complexities of local taxation

The global adoption of ISO 20022 promises to usher in a new era of streamlined, efficient, and secure international payments. The standard offers the following benefits in cross-border settlements:
● Global interoperability and standardization
Achieving seamless cross-border transactions involves collaboration, common standards, and enhanced regulatory frameworks. This requires complex interoperability between stakeholders, including harmonizing procedures like know-your-customer, currency conversion, and legal jurisdiction.
ISO 20022 holds the potential to significantly reduce friction in cross-border payments through two important mechanisms.
- Central banks that share a common messaging standard will be able to conduct more transactions and exchange richer information crucial for clearing, including KYC data and AML/CFT reporting.
- Even if a few major institutions embrace this international standard for essential financial infrastructure, it can incentivize payment providers to modernize their messaging systems and adopt new standards; in other words, it can cause a ripple effect nudging a wider adoption.
● Greater automation & improved straight-through processing (STP)
Standardized and structured data enable financial institutions to automate data validation, reconciliation, and processing, eliminating the need for manual reviews or corrections. This streamlined approach enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and accelerates transaction timelines.
Also, in the ISO 20022 payments industry, efficiency is gauged by the level of STP, representing the percentage of transactions smoothly processed from start to finish without manual intervention. In simple words, ISO 20022 creates a cascade of benefits – granular data leads to enhanced data-driven insights, data integration, standardization, and interoperability, which fuels automation, improving Straight Through Processing (STP) rates and reducing maintenance costs for different formats.
● Enhanced compliance and fraud prevention
ISO 20022 payment messages improve fraud prevention capabilities and streamline regulatory reporting activities by incorporating specific elements like purpose codes, regulatory reporting, and tax identification.
This comprehensive approach offers a clearer view of an institution’s transactions and complements existing analytics tools, simplifying ISO payment tracking. Consequently, ISO 20022 facilitates compliance with regulatory mandates for data completeness and processing quality.
Navigating the Hurdles in Implementing ISO 20022
The migration to ISO 20022 can become intricate due to various factors, primarily because its influence extends beyond cash transactions to the entire payments value chain. The rapid adoption of ISO 20022 in the global payments system poses substantial challenges for service providers.
● Legacy infrastructure
Legacy systems present obstacles in adopting ISO 20022 due to their incompatible language and stringent message formats, which even surpass the previous ISO 15022 standard.
Furthermore, ISO 20022 frequently updates its message standards and regularly releases new versions of message types, adding another layer of complexity to the ISO 20022 implementation process.
● Cost
Global banks currently face the pressure of constrained margins, primarily due to lower interest rates and other factors. As a result, their technology budgets have become limited. In this context, undertaking large-scale payment transformation projects becomes challenging for banks. Various other factors contribute to the financial burden faced by organizations looking to adopt the standard, such as:
- Upgrading infrastructure
- Data mapping and translation
- Training and skill development
- Testing and compliance
- Continuous updates and maintenance
● Timelines and deadlines
As the deadlines draw near, banks face competitive pressure to adopt the ISO 20022 standard and risk rendering their existing products and services inoperable if they fail to act. Finalizing an ISO 20022 implementation plan that thoroughly documents all payment scheme considerations and establishes milestones presents a challenge for banks
- Comprehensive data model
- Extensive message library
- Customization and business rules
- Impact on existing systems
Best Practices for ISO 20022 Migration
Banks and financial institutions are experiencing notable changes encompassing various aspects, such as operations, infrastructure, and technology. Successfully addressing these challenges will be pivotal for their success in transitioning to ISO 20022 and adapting to the dynamic financial landscape. The institutions should consider a few best practices before ISO 20022 migration.
● Understanding the standard and handling the ISO migration timeline
As anticipated with a significant global market change like ISO 20022, the involvement of numerous market participants has resulted in diverging timelines and implementation rulebooks over time.
Institutions must form a well-structured migration team to address this, defining clear roles, responsibilities, and communication channels. This team must work closely with stakeholders, including technology vendors, service providers, and industry bodies, to remain informed about the latest standards, guidelines, and best practices for ISO 20022 implementation.
The team must have a comprehensive understanding of the ISO 20022 standard, its data model, and message types before initiating the ISO migration process.
● Performing a thorough impact analysis
Conduct a thorough impact analysis to understand how ISO 20022 migration will affect the organization’s systems, processes, stakeholders, interfaces, data mapping, and compliance requirements, among other aspects.
For example, one of the most significant challenges during ISO migration is data truncation, where data is lost when switching from legacy to new standards. Data truncation can lead to payment processing errors.
For instance, if the famous Spanish painter Pablo Picasso were to receive a payment today, the payment would be addressed to “Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso” (a lengthy name indeed!) which would not be a problem in ISO 20022 but may be cut off when converted to MT format, resulting in the name being recorded as “Pablo Diego José Francisco,” potentially raising compliance concerns.
To effectively address this challenge, banks must prioritize solutions capable of handling data truncation and efficiently managing transaction data.
● Engage with technology partners and tools
Many financial institutions heavily rely on legacy systems, which can be complex and costly to update and meet new requirements. Opting for a partner with a proven solution, including various messaging protocols and seamless integration in existing infrastructure, is vital for completing the ISO 20022 migration.
● Invest in staff training and awareness
Financial institutions must invest in providing training and skill development programs to empower staff with the knowledge to work effectively with the ISO 20022 ecosystem.
Training should cover ISO 20022 fundamentals, message types, data elements, and mapping for various user groups: business users, IT teams, operations staff, and compliance officers.
Techwave’s ISO 20022 Messaging Standard and Cross-Border Payment and Data Management Services
It’s clear that ISO 20022 standard is the way forward. While the benefits are impressive, the challenges are overwhelming but not unbeatable. A payments data management service provider can help banks and financial institutions implement the best practices and address the obstacles effectively. Techwave has expertise in the cross-border payments domain and assists in streamlining all these best practices to support you effectively with ISO 20022 Payments Data Management, App Modernization, and API Ecosystem Management services.



